A Primer on the NERC Regional Entities
Regional Entities | ERO Enterprise
A regional entity (RE) in the North American power transmission grid is a regional organization representing all segments of the electric industry: electric utilities (investor-owned, cooperatives, state, regional, and municipal), federal agencies, independent power producers, power market operators, and end-users of the energy. North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) delegates to REs authority to enforce reliability standards (which NERC has throughout the contiguous United States), collectively REs, together with NERC, are known as an “ERO Enterprise” (from the Electric Reliability Organization).
NERC and the Regional Entities are committed to the following:
- clear and consistent guidance across the ERO Enterprise
- sharing information, knowledge, and resources across the ERO Enterprise
- developing and sharing harmonized messages across ERO Enterprise communications
- working together as one team and honoring each of their roles
- actively supporting ERO Enterprise activities while eliminating unnecessary duplication of work
- collaborating in developing
- supporting innovation, initiatives, and the sharing of best practices across the ERO Enterprise
History of the Regional Entities
The regional entities, at the bottom of the structure for the development and enforcement of the reliability standards for the US electric grid, were established by Section 215 of the Federal Power Act as amended by the Energy Policy Act of 2005. The statute tried to mimic the balance of power between the federal and state authorities in the US, with REs playing the role of regional (state-like) components.
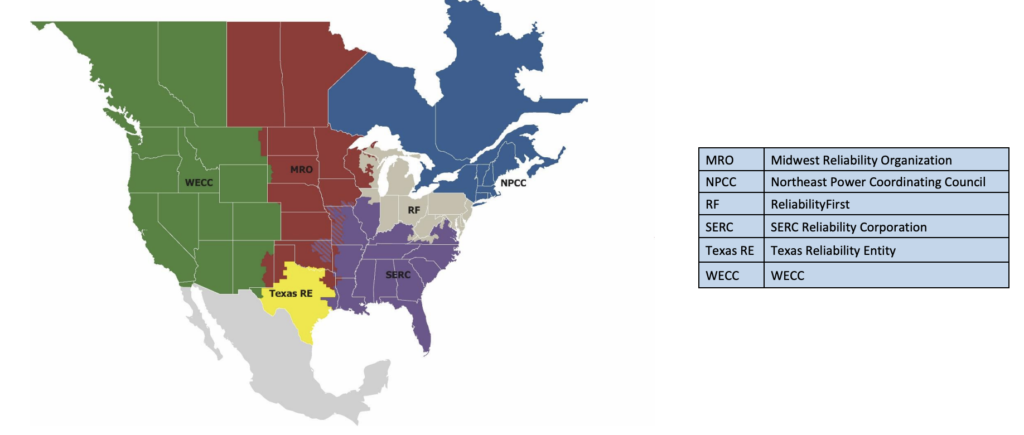
As of 2023, there are six regional entities:
- Midwest Reliability Organization (MRO);
- Northeast Power Coordinating Council (NPCC);
- ReliabilityFirst (RF);
- SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC);
- Texas Reliability Entity (Texas RE);
- Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC).
The original map of the NERC regional entities included two entities that no longer exist:
- Southwest Power Pool regional entity operation was dissolved in 2018 (by merging into MRO),
- Florida Reliability Coordinating Council was dissolved in July 2019 (by merging into SERC)

What is the Function of the NERC Regional Entities?
The reliability standard development process had Regional Entities developing regional standards to be approved by NERC and FERC. By 2010, the process was slow: just nine standards were developed, all by the WECC.
An RE approves the transmission plans and chooses the projects for regional (as opposed to per-local-pricing-zone) cost allocation.
One of the important roles of an RE is suggesting to NERC (and FERC) to include the facilities into – or exclude from – the list of “elements” that constitute the bulk-power system (BPS, also known as a “bulk electric system”, BES), subject to the oversight of the NERC.
As the reliability and security ecosystem continues to change, the ERO Enterprise is explicitly committed to its collective success in achieving its vision of a highly reliable and secure North American BPS.
Share
Regional Entities | ERO Enterprise
A regional entity (RE) in the North American power transmission grid is a regional organization representing all segments of the electric industry: electric utilities (investor-owned, cooperatives, state, regional, and municipal), federal agencies, independent power producers, power market operators, and end-users of the energy. North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) delegates to REs authority to enforce reliability standards (which NERC has throughout the contiguous United States), collectively REs, together with NERC, are known as an “ERO Enterprise” (from the Electric Reliability Organization).
NERC and the Regional Entities are committed to the following:
- clear and consistent guidance across the ERO Enterprise
- sharing information, knowledge, and resources across the ERO Enterprise
- developing and sharing harmonized messages across ERO Enterprise communications
- working together as one team and honoring each of their roles
- actively supporting ERO Enterprise activities while eliminating unnecessary duplication of work
- collaborating in developing
- supporting innovation, initiatives, and the sharing of best practices across the ERO Enterprise
History of the Regional Entities
The regional entities, at the bottom of the structure for the development and enforcement of the reliability standards for the US electric grid, were established by Section 215 of the Federal Power Act as amended by the Energy Policy Act of 2005. The statute tried to mimic the balance of power between the federal and state authorities in the US, with REs playing the role of regional (state-like) components.
As of 2023, there are six regional entities:
- Midwest Reliability Organization (MRO);
- Northeast Power Coordinating Council (NPCC);
- ReliabilityFirst (RF);
- SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC);
- Texas Reliability Entity (Texas RE);
- Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC).
The original map of the NERC regional entities included two entities that no longer exist:
- Southwest Power Pool regional entity operation was dissolved in 2018 (by merging into MRO),
- Florida Reliability Coordinating Council was dissolved in July 2019 (by merging into SERC)
What is the Function of the NERC Regional Entities?
The reliability standard development process had Regional Entities developing regional standards to be approved by NERC and FERC. By 2010, the process was slow: just nine standards were developed, all by the WECC.
An RE approves the transmission plans and chooses the projects for regional (as opposed to per-local-pricing-zone) cost allocation.
One of the important roles of an RE is suggesting to NERC (and FERC) to include the facilities into – or exclude from – the list of “elements” that constitute the bulk-power system (BPS, also known as a “bulk electric system”, BES), subject to the oversight of the NERC.
As the reliability and security ecosystem continues to change, the ERO Enterprise is explicitly committed to its collective success in achieving its vision of a highly reliable and secure North American BPS.
Just Getting Started with Nerc? Check Out Some of Our Resources
NERC Common Questions and Answers
What is the difference between FERC and NERC? The Federal...
Read MoreNERC Standards: NERC CIP Explained for the Energy Sector
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) mandate encompasses technical...
Read More













