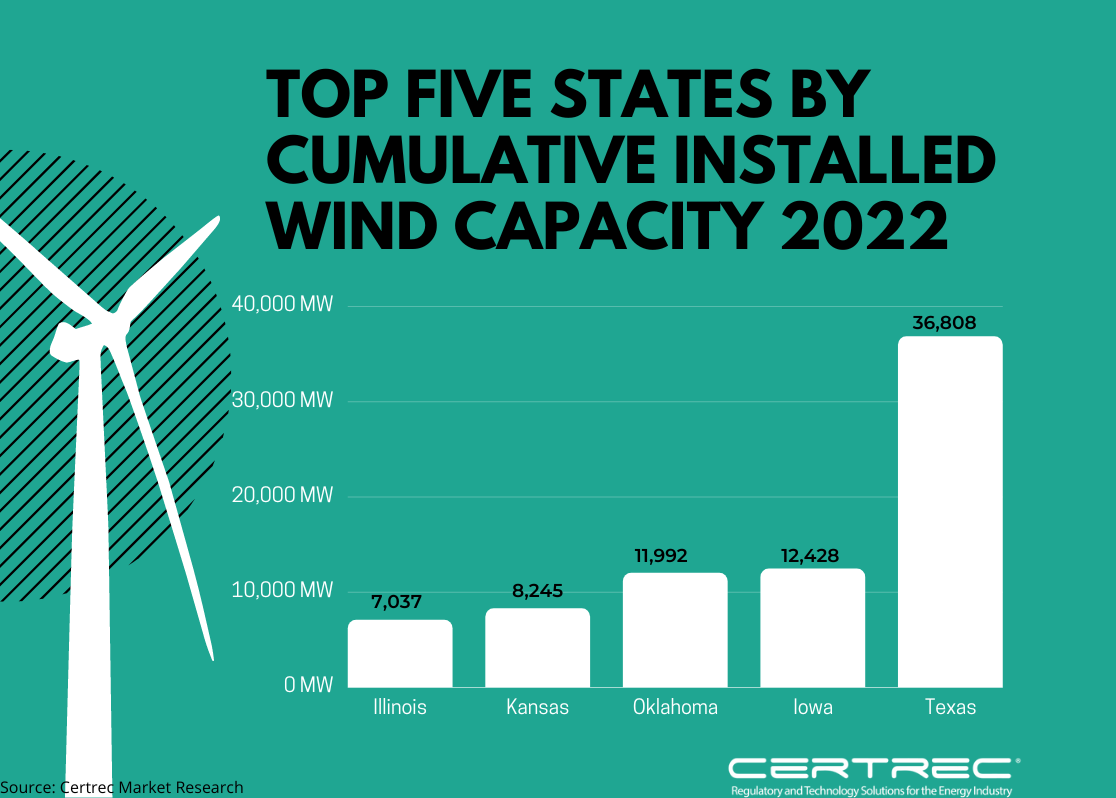
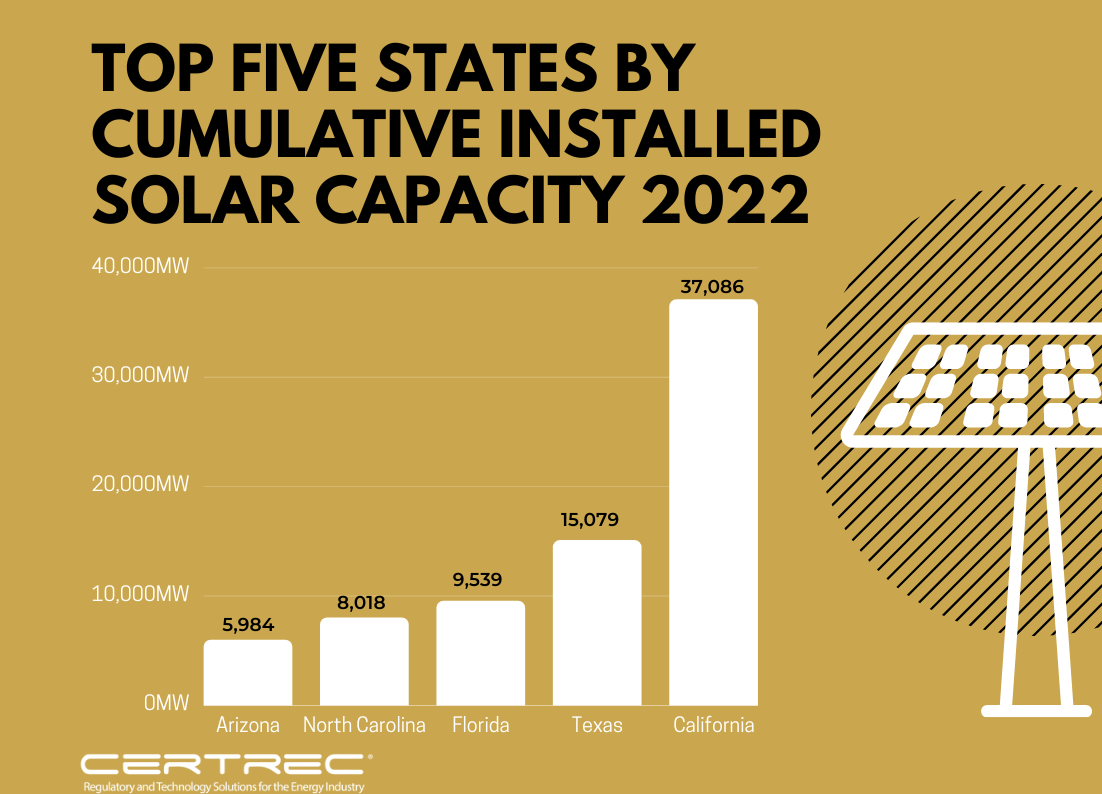
Certrec’s Hydro Market Research
Hydro Market Data
Hydroelectricity is one of the most popular renewable energy generation technologies for many reasons. It does not emit greenhouse gases or toxic waste and it’s one of the cheapest ways to generate electricity (running water). About a fifth of the world’s total electricity comes from hydro power and it is employed by more than 60 countries around the world. From water management, flood control, and its ability to respond to fluctuations in electricity — hydro power is increasingly popular.
In 2020, the hydro power installed capacity reached 1330 GW and it is anticipated to install approximately 1520 GW by 2027, at a CAGR of 1.93% during the forecast period of 2022 – 2027. Like with most markets, COVID-19 has significantly impacted the global hydro power market. Some projects are expected to be delayed during the forecast period due to lock-down measures and supply chain issues. Still, factors such as the increasing number of new hydro power projects and the rising demand for reliable electricity are expected to drive the market.
Large hydro power (greater than 100MW) is likely to be the largest segment. This is possible because of increasing investment in large hydro power and pumped storage projects alongside several major countries’ efforts to reach renewable energy targets and utilize cleaner energy sources.
Also, new technology trends are expected to increase hydro power generation and provide great opportunities for the hydro market in the next few years. Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market with the majority of the demand coming from countries like China, India, and Japan.
The high initial investment cost of hydroelectric infrastructure and safety concerns as this technology develops can restrict the worldwide market. Though it is a renewable energy source and is environmentally friendly, creating new hydroelectric facilities is difficult due to strict state and federal regulations and a lack of suitable locations. Current industry players are looking to upgrade facilities as the call for electricity increases.
The History of Hydro Energy in the United States
The use of water to generate power is one of the oldest methods humans have used to create power. Hydro power can be observed in methods of irrigation. It can also be observed in the process of grinding wheat into flour thousands of years ago.
Primitive versions of the modern hydro power turbine were pioneered by French hydraulic and military engineer, Bernard Forest de Bélidor. In the mid-1700s he wrote his book Architecture Hydraulique.
The alternating current is the method used today to generate electricity. Through this method, power can be transmitted across long distances. This breakthrough resulted in the first U.S. commercial installation: Redlands Power Plant. The plant is located in California and began generating power in 1893.
In 1902, the Bureau of Reclamation was established in the United States. This governmental agency provided water resource management to the western areas of the United States. Today, the Bureau of Reclamation is the second largest producer of hydro power in the nation.
The 20th saw the development of many large-scale hydro power projects in the U.S. President Roosevelt’s New Deal created construction programs that tripled the capacity of energy produced by hydro power from just 20 years earlier.
Perhaps the most famous hydroelectric project, Hoover Dam, began construction in 1936. Built on the Colorado River, this ambitious project was created to provide irrigation water, control floods, and supply power to Arizona and Nevada.
Today, the demand for non-carbon energy alternatives is greater than ever. The United States is utilizing hydro power to meet increasing energy needs and meet carbon reduction goals.
How do Hydro Turbines Work?
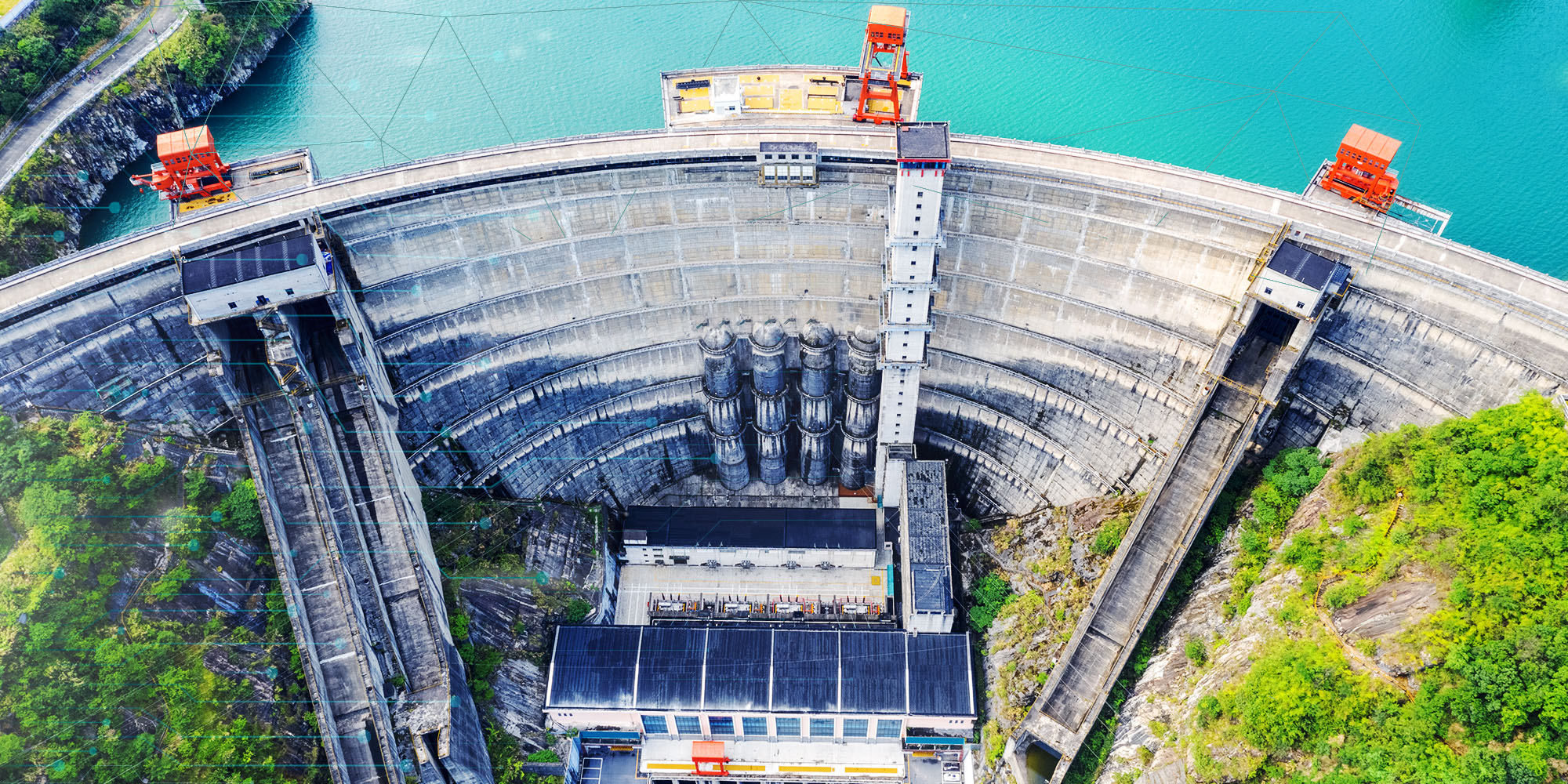
Hydroelectricity is produced by utilizing the gravity of falling water to turn a turbine. For this reason, dams are built on large rivers with drops in elevation. The dam stores lots of water behind it in the reservoir. Near the bottom of the dam wall, there is the water intake. Gravity causes it to fall through the penstock inside the dam.
At the end of the penstock, there is a turbine propeller, which is turned by the moving water. The shaft from the turbine goes up into the generator, which produces the power. Power lines are connected to the generator that carries electricity to its destination. The water continues past the propeller through the tailrace into the river past the dam.
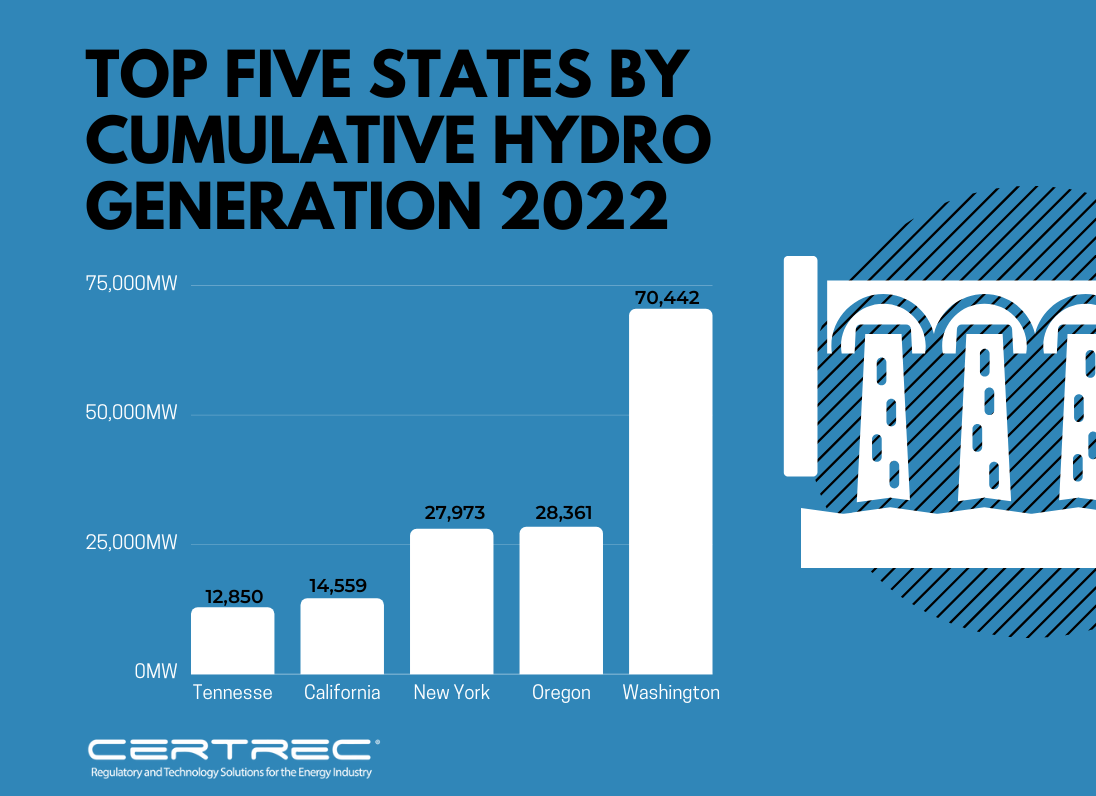
The five states with the most cumulative hydro generation are:
- Washington (70,442 MW)
- Oregon (28,361 MW)
- New York (27,973 MW)
- California (14,559 MW)
- Tennessee (12,850 MW)
Want more information on hydro plants?
Click here to see that largest hydro plants in the United States.
Share
Hydro Market Data
Hydroelectricity is one of the most popular renewable energy generation technologies for many reasons. It does not emit greenhouse gases or toxic waste and it’s one of the cheapest ways to generate electricity (running water). About a fifth of the world’s total electricity comes from hydro power and it is employed by more than 60 countries around the world. From water management, flood control, and its ability to respond to fluctuations in electricity — hydro power is increasingly popular.
In 2020, the hydro power installed capacity reached 1330 GW and it is anticipated to install approximately 1520 GW by 2027, at a CAGR of 1.93% during the forecast period of 2022 – 2027. Like with most markets, COVID-19 has significantly impacted the global hydro power market. Some projects are expected to be delayed during the forecast period due to lock-down measures and supply chain issues. Still, factors such as the increasing number of new hydro power projects and the rising demand for reliable electricity are expected to drive the market.
Large hydro power (greater than 100MW) is likely to be the largest segment. This is possible because of increasing investment in large hydro power and pumped storage projects alongside several major countries’ efforts to reach renewable energy targets and utilize cleaner energy sources.
Also, new technology trends are expected to increase hydro power generation and provide great opportunities for the hydro market in the next few years. Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market with the majority of the demand coming from countries like China, India, and Japan.
The high initial investment cost of hydroelectric infrastructure and safety concerns as this technology develops can restrict the worldwide market. Though it is a renewable energy source and is environmentally friendly, creating new hydroelectric facilities is difficult due to strict state and federal regulations and a lack of suitable locations. Current industry players are looking to upgrade facilities as the call for electricity increases.
The History of Hydro Energy in the United States
The use of water to generate power is one of the oldest methods humans have used to create power. Hydro power can be observed in methods of irrigation. It can also be observed in the process of grinding wheat into flour thousands of years ago.
Primitive versions of the modern hydro power turbine were pioneered by French hydraulic and military engineer, Bernard Forest de Bélidor. In the mid-1700s he wrote his book Architecture Hydraulique.
The alternating current is the method used today to generate electricity. Through this method, power can be transmitted across long distances. This breakthrough resulted in the first U.S. commercial installation: Redlands Power Plant. The plant is located in California and began generating power in 1893.
In 1902, the Bureau of Reclamation was established in the United States. This governmental agency provided water resource management to the western areas of the United States. Today, the Bureau of Reclamation is the second largest producer of hydro power in the nation.
The 20th saw the development of many large-scale hydro power projects in the U.S. President Roosevelt’s New Deal created construction programs that tripled the capacity of energy produced by hydro power from just 20 years earlier.
Perhaps the most famous hydroelectric project, Hoover Dam, began construction in 1936. Built on the Colorado River, this ambitious project was created to provide irrigation water, control floods, and supply power to Arizona and Nevada.
Today, the demand for non-carbon energy alternatives is greater than ever. The United States is utilizing hydro power to meet increasing energy needs and meet carbon reduction goals.
How do Hydro Turbines Work?
Hydroelectricity is produced by utilizing the gravity of falling water to turn a turbine. For this reason, dams are built on large rivers with drops in elevation. The dam stores lots of water behind it in the reservoir. Near the bottom of the dam wall, there is the water intake. Gravity causes it to fall through the penstock inside the dam.
At the end of the penstock, there is a turbine propeller, which is turned by the moving water. The shaft from the turbine goes up into the generator, which produces the power. Power lines are connected to the generator that carries electricity to its destination. The water continues past the propeller through the tailrace into the river past the dam.
The five states with the most cumulative hydro generation are:
- Washington (70,442 MW)
- Oregon (28,361 MW)
- New York (27,973 MW)
- California (14,559 MW)
- Tennessee (12,850 MW)
Want more information on hydro plants?
Click here to see that largest hydro plants in the United States.