The U.S. requires resource-efficient and economical solutions to meet ever-increasing energy demands. The nuclear industry is looking for innovative approaches to solve this issue. High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) has developed as a solution to nuclear fuel needs. It aims to fulfill the steady growth of energy requirements in the United States. The basic structure of power reactors may undergo a complete transformation thanks to HALEU nuclear fuel. The implementation of HALEU as nuclear fuel includes better reactor efficiency and the creation of contemporary generation reactor technology.
Understanding HALEU: Composition and Capabilities
The enrichment process of uranium produces HALEU by raising uranium-235 levels (U-235) within 5% to 20%, exceeding normal LEU concentrations at 3–5%. The elevated concentration level of HALEU enables its function as a multipurpose fuel material that powers Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), microreactors, and next-generation fast reactors. Besides requiring denser fuel energy content, these advanced designs need increased operational duration along with maximum thermal efficiency capabilities and reduced physical dimensions.
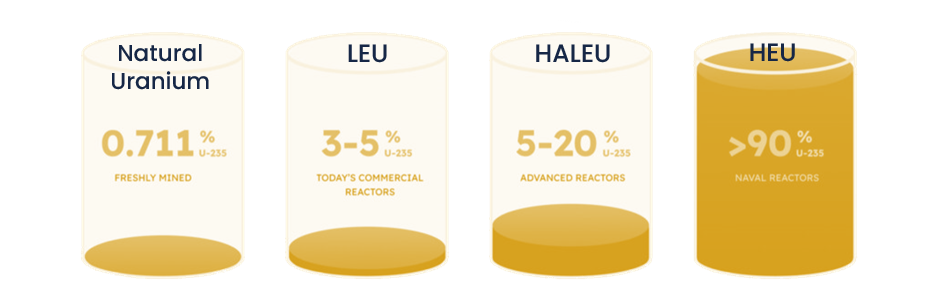
Although HALEU belongs to the U-235 enriched uranium class, it separates itself from the highly enriched uranium category (HEU) that requires greater proliferation control measures. HALEU yields optimal performance levels through its regulatory-safe enrichment limits, which positions it as an excellent candidate for civilian and commercial reactor systems.
Key Benefits of HALEU for the Nuclear Sector
HALEU offers multiple advantages to nuclear facilities according to the following essential benefits:
- Increased Fuel Efficiency: Lower U-235 concentration enables HALEU to boost cycle duration between refueling periods as it produces more energy from each fuel unit.
- Support for Advanced Reactor Designs: HALEU works as a big support to advanced energy reactors due to its capabilities with new innovative reactor designs, which need increased temperatures alongside concentrated fuel materials.
- Reduced Waste Generation: Through improved fuel efficiency, HALEU reduces the amount of nuclear waste that requires storage because it enables more efficient use of the spent fuel material.
- Enhanced Load-Following Capabilities: HALEU-powered reactors demonstrate higher efficiency in adjusting power output frequencies, which supports power grid operations with intermittent renewable sources.
- Smaller Reactor Footprints: Higher energy density permits nuclear reactor cores to become more compact, therefore making them useful for military bases, remote facilities, and industrial installations.
Infrastructure and Regulatory Challenges
The major challenge preventing HALEU supply expansion exists in its broad-scale production requirements. Currently the energy sector doesn’t possess the commercial-scale infrastructure required to fully depend on HALEU, and Russia has been the primary supplier of this element. Western nations, especially the U.S. and members of the European Union, have intensified their efforts toward creating national HALEU fuel capabilities due to their dependence on Russia.
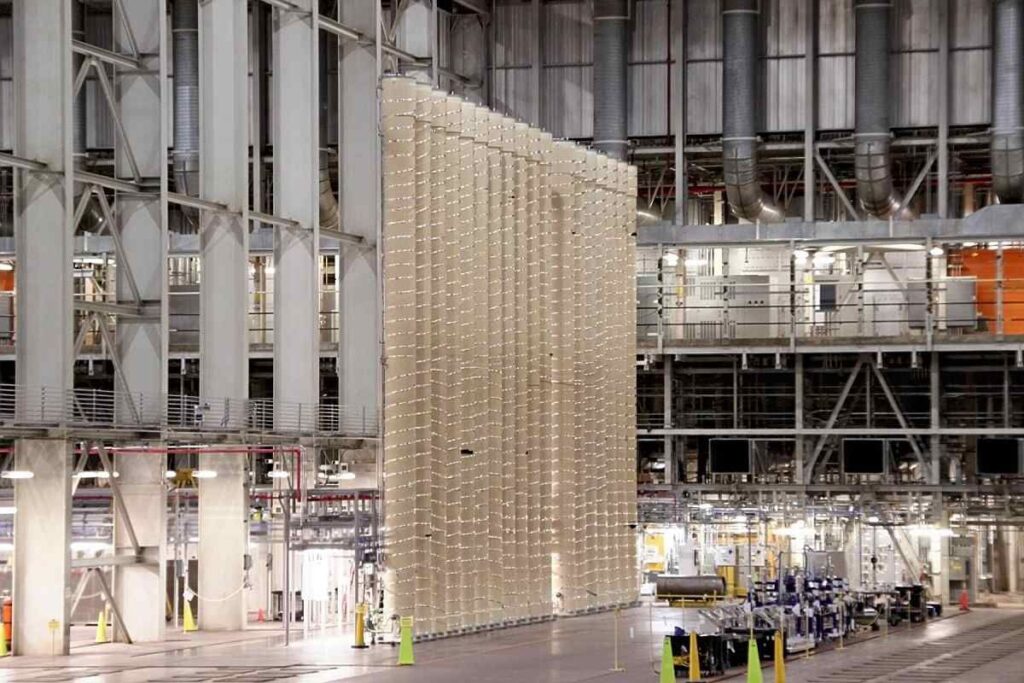

The HALEU Availability Program established by the U.S. Department of Energy works to build domestic enrichment capabilities while assuring a dependable fuel supply. Private enterprise company Centrus Energy starts implementing HALEU projects after receiving NRC authorization to process uranium to 20% U-235 at its Ohio Piketon facility. The commercial sector operates HALEU production at an initial stage where only small amounts are available for market.
Conclusion
The nuclear industry will undergo transformation through HALEU since it can create safer, smaller, efficient reactors designed for modern energy market needs. The multiple advantages of HALEU fuel extend to increased fuel utilization periods alongside superior reactor financial performance and minimized waste amounts. The full utilization of HALEU depends on solving major challenges during production and obtaining regulatory acceptance. The current HALEU development activities demonstrate strong potential to establish HALEU as the fundamental building block for a new nuclear power expansion that meets worldwide climate targets and power grid requirements.
Disclaimer: Any opinions expressed in this blog do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Certrec. This content is meant for informational purposes only.