What are NERC Reliability Standards?
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s (NERC) Reliability Standards define the requirements for planning process and operations of the Bulk Electric System (BES). These standards are subject to enforcement within the United States and parts of Canada and Mexico. Reliability Standards establish threshold requirements for assuring the Bulk Electric System is planned, operated, and maintained to minimize risks of cascading failures, avoid damage to major equipment, or limit interruptions of the Bulk Power System (BPS).
The NERC standards consist of almost 100 standards across 14 different disciplines. NERC monitors and enforces compliance with these standards through six regional entities. These regional entities are:
- Midwest Reliability Organization (MRO)
- Northeast Power Coordinating Council (NPCC)
- Reliability First (RF)
- SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC)
- Texas Reliability Entity (Texas RE)
- Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC)
NERC Pillars for Success
The NERC reliability standards are built around four pillars for continued success. These pillars were developed in collaboration with the six regional entities. You can read more about NERC’s core values and strategies for success here. As defined by NERC, these pillars are:
- Reliability – to address events and identifiable risks, thereby ensuring the reliability of the BES
through proper mitigation and remediation. - Assurance – to provide assurance to the public, industry, and government for the reliable
performance of the BES. - Learning – to promote learning and continuous improvement of operations and adapt to lessons
learned for BES reliability. - Risk-Based Approach – to focus attention, resources, and actions on issues most important to BES
reliability.
Failure of NERC-registered entities to comply with these standards could result in grievous fines based on the severity and duration of the violation. When an organization is in violation of standards, the corresponding regional entities assess penalties and monitor approved mitigation plans for compliance. Listed below are the NERC Reliability Standards currently subject to enforcement and their purpose.
The NERC reliability standards are built around four pillars for continued success. These pillars were developed in collaboration with the six regional entities. You can read more about NERC’s core values and strategies for success here. As defined by NERC, these pillars are:
- Reliability – to address events and identifiable risks, thereby ensuring the reliability of the BES
through proper mitigation and remediation. - Assurance – to provide assurance to the public, industry, and government for the reliable
performance of the BES. - Learning – to promote learning and continuous improvement of operations and adapt to lessons
learned for BES reliability. - Risk-Based Approach – to focus attention, resources, and actions on issues most important to BES
reliability.
Failure of NERC-registered entities to comply with these standards could result in grievous fines based on the severity and duration of the violation. When an organization is in violation of standards, the corresponding regional entities assess penalties and monitor approved mitigation plans for compliance. Listed below are the NERC Reliability Standards currently subject to enforcement and their purpose.
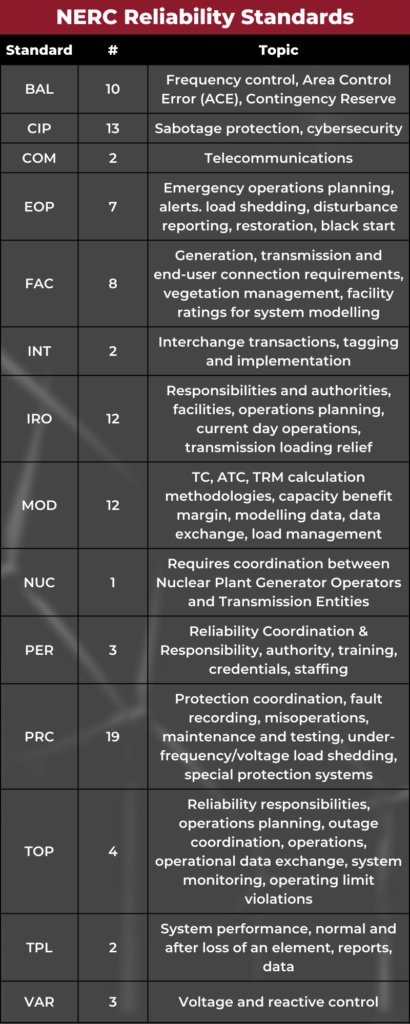
The NERC Reliability Standards:
Resource and Demand Balancing (BAL)
- BAL-001-2: Real Power Balancing Control Performance
- Purpose: To control Interconnection frequency within defined limits.
- BAL-001-TRE-1: Primary Frequency Response in the ERCOT Region
- Purpose: To maintain Interconnection steady-state frequency within defined limits
- BAL-001-TRE-2: Primary Frequency Response in the ERCOT Region
- Purpose: To maintain Interconnection steady-state frequency within defined limits.
- BAL-002-3: Disturbance Control Standard – Contingency Reserve for Recovery from a Balancing Contingency Event
- Purpose: To ensure the Balancing Authority or Reserve Sharing Group balances resources and demand and returns the Balancing Authority’s or Reserve Sharing Group’s Area Control Error to defined values (subject to applicable limits) following a Reportable Balancing Contingency Event.
- BAL-002-WECC-2a: Contingency Reserve
- Purpose: To specify the quantity and types of Contingency Reserve required to ensure reliability under normal and abnormal conditions.
- BAL-002-WECC-3: Contingency Reserve
- Purpose: To specify the quantity and types of Contingency Reserve required to ensure reliability under normal and abnormal conditions.
- BAL-003-2: Frequency Response and Frequency Bias Setting
- Purpose: To require sufficient Frequency Response from the Balancing Authority (BA) to maintain Interconnection Frequency within predefined bounds by arresting frequency deviations and supporting frequency until the frequency is restored to its scheduled value. To provide consistent methods for measuring Frequency Response and determining the Frequency Bias Setting.
- BAL-0040-WECC-3: Automatic Time Error Correction
- Purpose: To maintain Interconnection frequency and to ensure that Time Error Corrections and Primary Inadvertent Interchange (PII) payback are effectively conducted in a manner that does not adversely affect the reliability of the Interconnection.
- BAL-005-1: Balancing Authority Control
- Purpose: This standard establishes requirements for acquiring data necessary to calculate Reporting Area Control Error (Reporting ACE). The standard also specifies a minimum periodicity, accuracy, and availability requirement for acquisition of the data and for providing the information to the System Operator.
- BAL-502-RF-03: Planning Resource Adequacy Analysis, Assessment and Documentation
- Purpose: To establish common criteria, based on “one day in ten year” loss of Load expectation principles, for the analysis, assessment and documentation of Resource Adequacy for Load in the ReliabilityFirst Corporation (RF) region
Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP)
- CIP-002-5.1a: Cyber Security – BES Cyber System Categorization
- Purpose: To identify and categorize BES Cyber Systems and their associated BES Cyber Assets for the application of cyber security requirements commensurate with the adverse impact that loss, compromise, or misuse of those BES Cyber Systems could have on the reliable operation of the BES. Identification and categorization of BES Cyber Systems support appropriate protection against compromises that could lead to misoperation or instability in the BES.
- CIP-003-8: Cyber Security – Security Management Controls
- Purpose: To specify consistent and sustainable security management controls that establish responsibility and accountability to protect BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-004-6: Cyber Security – Personnel & Training
- Purpose: To minimize the risk against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES) from individuals accessing BES Cyber Systems by requiring an appropriate level of personnel risk assessment, training, and security awareness in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems.
- CIP-005-7: Cyber Security – Electronic Security Perimeter(s)
- Purpose: To manage electronic access to BES Cyber Systems by specifying a controlled Electronic Security Perimeter in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the BES.
- CIP-006-6: Cyber Security – Physical Security of BES Cyber Systems
- Purpose: To manage physical access to Bulk Electric System (BES) Cyber Systems by specifying a physical security plan in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the BES.
- CIP-007-6: Cyber Security – System Security Management
- Purpose: To manage system security by specifying select technical, operational, and procedural requirements in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-008-6: Cyber Security – Incident Reporting and Response Planning
- Purpose: To mitigate the risk to the reliable operation of the BES as the result of a Cyber Security Incident by specifying incident response requirements.
- CIP-009-6: Cyber Security – Recovery Plans for BES Cyber Systems
- Purpose: To recover reliability functions performed by BES Cyber Systems by specifying recovery plan requirements in support of the continued stability, operability, and reliability of the BES.
- CIP-10-4: Cyber Security – Configuration Change Management and Vulnerability Assessments
- Purpose: To prevent and detect unauthorized changes to BES Cyber Systems by specifying configuration change management and vulnerability assessment requirements in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems from compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-011-2: Cyber Security – Information Protection
- Purpose: To prevent unauthorized access to BES Cyber System Information by specifying information protection requirements in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-012-1: Cyber Security – Communications between Control Centers
- Purpose: To protect the confidentiality and integrity of Real-time Assessment and Real-time monitoring data transmitted between Control Centers.
- CIP-013-2: Cyber Security – Supply Chain Risk Management
- Purpose: To mitigate cyber security risks to the reliable operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) by implementing security controls for supply chain risk management of BES Cyber Systems.
- CIP-014-3: Physical Security
- Purpose: To identify and protect Transmission stations and Transmission substations, and their associated primary control centers, that if rendered inoperable or damaged as a result of a physical attack could result in instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading within an
Interconnection
- Purpose: To identify and protect Transmission stations and Transmission substations, and their associated primary control centers, that if rendered inoperable or damaged as a result of a physical attack could result in instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading within an
Communications (COM)
- COM-001-3: Communications
- Purpose: To establish Interpersonal Communication capabilities necessary to maintain reliability.
- COM-002-4: Operating Personnel Communications Protocols
- Purpose: To improve communications for the issuance of Operating Instructions with predefined communications protocols to reduce the possibility of miscommunication that could lead to action or inaction harmful to the reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES)
Emergency Preparedness and Operations (EOP)
- EOP-004-4: Event Reporting
- Purpose: To improve the reliability of the Bulk Electric System by requiring the reporting of events by Responsible Entities.
- EOP-005-3: System Restoration from Blackstart Resources
- Purpose: Ensure plans, Facilities, and personnel are prepared to enable System restoration from Blackstart Resources to ensure reliability is maintained during restoration and priority is placed on restoring the Interconnection.
- EOP-006-3: System Restoration Coordination
- Purpose: Ensure plans are established and personnel are prepared to enable effective coordination of the System restoration process to ensure reliability is maintained during restoration and priority is placed on restoring the Interconnection.
- EOP-008-2: Loss of Control Center Functionality
- Purpose: Ensure continued reliable operations of the Bulk Electric System (BES) in the event that a control center becomes inoperable.
- EOP-10-1: Geomagnetic Disturbance Operations
- Purpose: To mitigate the effects of geomagnetic disturbance (GMD) events by implementing Operating Plans, Processes, and Procedures.
- EOP-011-1: Emergency Operations
- Purpose: To address the effects of operating Emergencies by ensuring each Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority has developed Operating Plan(s) to mitigate operating Emergencies, and that those plans are coordinated within a Reliability Coordinator Area.
- EOP-011-2: Emergency Preparedness and Operations
- Purpose: To ensure each Transmission Operator, Balancing Authority, and Generator Owner has developed plan(s) to mitigate and prepare for operating Emergencies; and that Operating Plans are coordinated within a Reliability Coordinator Area.
Facilities Design, Connections, and Maintenance (FAC)
- FAC-001-3: Facility Interconnection Requirements
- Purpose: To avoid adverse impacts on the reliability of the Bulk Electric System, Transmission Owners and applicable Generator Owners must document and make Facility interconnection requirements available so that entities seeking to interconnect will have the necessary information.
- FAC-002-3: Facility Interconnection Studies
- Purpose: To study the impact of interconnecting new or materially modified Facilities on the Bulk Electric System.
- FAC-003-4: Transmission Vegetation Management
- Purpose: To maintain a reliable electric transmission system by using a defense-in-depth strategy to manage vegetation located on transmission rights of way (ROW) and minimize encroachments from vegetation located adjacent to the ROW, thus preventing the risk of those vegetation- related outages that could lead to Cascading.
- FAC-008-5: Facility Ratings
- Purpose: To ensure that Facility Ratings used in the reliable planning and operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on technically sound principles. A Facility Rating is essential for the determination of System Operating Limits.
- FAC-010-3: System Operating Limits Methodology for the Planning Horizon
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operating Limits (SOLs) used in the reliable planning of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on an established methodology or methodologies.
- FAC-011-3: System Operating Limits Methodology got the Operation Horizon
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operating Limits (SOLs) used in the reliable operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on an established methodology or methodologies.
- FAC-014-2: Establish and Communicate System Operating Limits
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operating Limits (SOLs) used in the reliable planning and operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on an established methodology or methodologies.
- FAC-501-WECC-2: Transmission Maintenance
- Purpose: To ensure the Transmission Owner of a transmission path identified in Attachment B, Major WECC Transfer Paths in the Bulk Electric System, including associated facilities has a Transmission Maintenance and Inspection Plan (TMIP); and performs and documents maintenance and inspection activities in accordance with the TMIP.
Interchange Scheduling and Coordination (INT)
- INT-006-5: Evaluation of Interchange Transactions
- Purpose: To ensure that responsible entities conduct a reliability assessment of each Arranged Interchange before it is implemented.
- INT-009-3: Implementation of Interchange
- Purpose: To ensure that Balancing Authorities implement the Interchange as agreed upon in the Interchange confirmation process.
Interconnection Reliability Operations and Coordination (IRO)
- IRO-001-4: Reliability Coordination – Responsibilities and Authorities
- Purpose: To establish the responsibility of Reliability Coordinators to act or direct other entities to act.
- IRO-002-4: Reliability Coordination – Monitoring and Analysis
- Purpose: Provide System Operators with the capabilities necessary to monitor and analyze data needed to perform their reliability functions.
- IRO-002-7: Reliability Coordination – Monitoring and Analysis
- Purpose: To provide System Operators with the capabilities necessary to monitor and analyze data needed to perform their reliability functions.
- IRO-006-5: Reliability Coordination – Transmission Loading Relief (TLR)
- Purpose: To ensure coordinated action between Interconnections when implementing Interconnection-wide transmission loading relief procedures to prevent or manage potential or actual SOL and IROL exceedances to maintain reliability of the bulk electric system.
- IRO-006-EAST-2: Transmission Loading Relief Procedure for the Eastern Connection
- Purpose: To coordinate action between Reliability Coordinators within the Eastern
Interconnection when implementing transmission loading relief procedures (TLR) for the Eastern Interconnection to prevent or manage potential or actual System Operating Limit (SOL) and Interconnection Reliability Operating Limit (IROL) exceedances to maintain reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- Purpose: To coordinate action between Reliability Coordinators within the Eastern
- IRO-006-WECC-3: Qualified Path Unscheduled Flow (USF) Relief
- Purpose: To mitigate flows on Qualified Paths to reliable levels during Real-time operations.
- IRO-008-2: Reliability Coordinator Operational Analyses and Real-time Assessments
- Purpose: Perform analyses and assessments to prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading.
- IRO-009-2 Reliability Coordinator Actions to Operate Within IROLs
- Purpose: To prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or cascading outages that adversely impact the reliability of the interconnection by ensuring prompt action to prevent or mitigate instances of exceeding Interconnection Reliability Operating Limits (IROLs).
- IRO-010-3: Reliability Coordinator Data Specification and Collection
- Purpose: To prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading outages that adversely impact reliability, by ensuring the Reliability Coordinator has the data it needs to monitor and assess the operation of its Reliability Coordinator Area.
- IRO-014-3: Coordination Among reliability Coordinators
- Purpose: To ensure that each Reliability Coordinator’s operations are coordinated such that they will not adversely impact other Reliability Coordinator Areas and to preserve the reliability benefits of interconnected operations.
- IRO-017-1: Outage Coordination
- Purpose: To ensure that outages are properly coordinated in the Operations Planning time horizon and Near-Term Transmission Planning Horizon.
- IRO-018-1(i): Reliability Coordinator Real-time Reliability Monitoring and Analysis
- Purpose: Establish requirements for Real-time monitoring and analysis capabilities to support reliable System operations.
Modeling, Data, and Analysis (MOD)
- MOD-001-1a: Available Transmission System Capability
- Purpose: To ensure that calculations are performed by Transmission Service Providers to maintain awareness of available transmission system capability and future flows on their own systems as well as those of their neighbors
- MOD-004-1: Capacity Benefit Margin
- Purpose: To promote the consistent and reliable calculation, verification, preservation, and use of Capacity Benefit Margin (CBM) to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-008-1: Transmission Reliability Margin Calculation Methodology
- Purpose: To promote the consistent and reliable calculations, verification, preservation, and use of Transmission Reliability Margin (TRM) to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-025-2: Verification and Data Reporting of Generator Real and Reactive Power Capability and Synchronous Condenser Reactive Power Capability
- Purpose: To ensure that accurate information on generator gross and net Real and Reactive Power capability and synchronous condenser Reactive Power capability is available for planning models used to assess Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability.
- MOD-026-1: Verification of Models and Data for Generator Excitation Control System or Plant Volt/Var Control Functions
- Purpose: To verify that the generator excitation control system or plant volt/var control function model (including the power system stabilizer model and the impedance compensator model) and the model parameters used in dynamic simulations accurately represent the generator excitation control system or plant volt/var control function behavior when assessing Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability.
- MOD-027-1: Verification of Models and Data for Turbine/Governor and Load Control or Active Power/Frequency Control Functions
- Purpose: To verify that the turbine/governor and load control or active power/frequency control model and the model parameters, used in dynamic simulations that assess Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability, accurately represent generator unit real power response to system frequency variations.
- MOD-028-2: Area Interchange Methodology
- Purpose: To increase consistency and reliability in the development and documentation of Transfer Capability calculations for short-term use performed by entities using the Area Interchange Methodology to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-029-2a: Rated System Path Methodology
- Purpose: To increase consistency and reliability in the development and documentation of transfer capability calculations for short-term use performed by entities using the Rated System Path Methodology to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-30-3: Flowgate Methodology
- Purpose: To increase consistency and reliability in the development and documentation of transfer capability calculations for short-term use performed by entities using the Flowgate Methodology to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-31-3: Demand and Energy Data
- Purpose: To provide authority for applicable entities to collect Demand, energy and related data to support reliability studies and assessments and to enumerate the responsibilities and obligations of requestors and respondents of that data.
- MOD-032-1: Data for Power System, Modeling and Analysis
- Purpose: To establish consistent modeling data requirements and reporting procedures for development of planning horizon cases necessary to support analysis of the reliability of the interconnected transmission system.
- MOD-033-2: Steady-State and Dynamic System Model Validation
- Purpose: To establish consistent validation requirements to facilitate the collection of accurate data and building of planning models to analyze the reliability of the interconnected transmission system.
Nuclear (NUC)
- NUC-001-4: Nuclear Plant Interface Coordination
- Purpose: This standard requires coordination between Nuclear Plant Generator Operators and Transmission Entities for the purpose of ensuring nuclear plant safe operation and shutdown.
Personnel Performance, Training, and Qualifications (PER)
- PER-003-2: Operating Personnel Credentials
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operators performing the reliability-related tasks of the Reliability Coordinator, Balancing Authority and Transmission Operator are certified through the NERC System Operator Certification Program when filling a Real- time operating position responsible for control of the Bulk Electric System.
- PER-005-2: Operations Personnel Training
- Purpose: To ensure that personnel performing or supporting Real-time operations on the Bulk Electric System are trained using a systematic approach.
- PER-006-1: Specific Training for Personnel
- Purpose: To ensure that personnel are trained on specific topics essential to reliability to perform or support Real-time operations of the Bulk Electric System.
Protection and Control (PRC)
- PRC-002-2: Disturbance Monitoring and Reporting Requirements
- Purpose: To have adequate data available to facilitate analysis of Bulk Electric System (BES) Disturbances.
- PRC-004-6: Protection System Misoperation Identification and Correction
- Purpose: Identify and correct the causes of Misoperations of Protection Systems for Bulk Electric System (BES) Elements.
- PRC-005-1.1b: Transmission and Generation Protection System Maintenance and Testing
- Purpose: To ensure all transmission and generation Protection Systems affecting the reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are maintained and tested.
- PRC-005-6: Protection System, Automatic Reclosing, and Sudden Pressure Relaying Maintenance
- Purpose: To document and implement programs for the maintenance of all Protection Systems, Automatic Reclosing, and Sudden Pressure Relaying affecting the reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES) so that they are kept in working order.
- PRC-006-5: Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding
- Purpose: To establish design and documentation requirements for automatic underfrequency load shedding (UFLS) programs to arrest declining frequency, assist recovery of frequency following underfrequency events and provide last resort system preservation measures.
- PRC-006-NPCC-2: Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding
- Purpose: The NPCC Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding (UFLS) regional Reliability Standard establishes more stringent and specific NPCC UFLS program requirements than the NERC continent–wide PRC–006 standard. The program is designed such that declining frequency is arrested and recovered in accordance with established NPCC performance requirements stipulated in this document.
- PRC-006-SERC-02: Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding Requirements
- Purpose: To establish consistent and coordinated requirements for the design, implementation, and analysis of automatic underfrequency load shedding (UFLS) programs among all SERC applicable entities.
- PRC-008-0: Implementation and Documentation of Underfrequency Load Shedding Equipment Maintenance Program
- Purpose: Provide last resort system preservation measures by implementing an Under Frequency Load Shedding (UFLS) program.
- PRC-010-2: Undervoltage Load Shedding
- Purpose: To establish an integrated and coordinated approach to the design, evaluation, and reliable operation of Undervoltage Load Shedding Programs (UVLS Programs).
- PRC-011-0: Undervoltage Load Shedding System Maintenance and Testing
- Purpose: Provide system preservation measures in an attempt to prevent system voltage collapse or voltage instability by implementing an Undervoltage Load Shedding (UVLS) program.
- PRC-012-2: Remedial Action Schemes
- Purpose: To ensure that Remedial Action Schemes (RAS) do not introduce unintentional or unacceptable reliability risks to the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- PRC-017-1: Remedial Action Scheme Maintenance and Testing
- Purpose: To ensure that all Remedial Action Schemes (RAS) are properly designed, meet performance requirements, and are coordinated with other protection systems. To ensure that
maintenance and testing programs are developed and misoperations are analyzed and corrected.
- Purpose: To ensure that all Remedial Action Schemes (RAS) are properly designed, meet performance requirements, and are coordinated with other protection systems. To ensure that
- PRC-018-1: Disturbance Monitoring Equipment Installation and Data Reporting
- Purpose: Ensure that Disturbance Monitoring Equipment (DME) is installed and that Disturbance data is reported in accordance with regional requirements to facilitate analyses of events.
- PRC-019-2: Coordination of Generating Unit or Plant Capabilities, Voltage Regulating Controls, and Protection
- Purpose: To verify coordination of generating unit Facility or synchronous condenser voltage regulating controls, limit functions, equipment capabilities and Protection System settings.
- PRC-023-4: Transmission Relay Loadability
- Purpose: Protective relay settings shall not limit transmission loadability; not interfere with system operators’ ability to take remedial action to protect system reliability and; be set to reliably detect all fault conditions and protect the electrical network from these faults.
- PRC-024-3: Frequency and Voltage Protection Settings for Generating Resources
- Purpose: To set protection such that generating resource(s) remain connected during defined frequency and voltage excursions in support of the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- PRC-025-2: Generator Relay Loadability
- Purpose: To set load-responsive protective relays associated with generation Facilities at a level to prevent unnecessary tripping of generators during a system disturbance for conditions that do not pose a risk of damage to the associated equipment.
- PRC-026-1: Relay Performance During Stable Power Swings
- Purpose: To ensure that load-responsive protective relays are expected to not trip in response to stable power swings during non-Fault conditions.
- PRC-027-1: Coordination of Protection Systems for Performance During Faults
- Purpose: To maintain the coordination of Protection Systems installed to detect and isolate Faults on Bulk Electric System (BES) Elements, such that those Protection Systems operate in the intended sequence during Faults.
Transmission Operations (TOP)
- TOP-001-5: Transmission Operations
- Purpose: To prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading outages that adversely impact the reliability of the Interconnection by ensuring prompt action to prevent or mitigate such occurrences.
- TOP-002-4: Operations Planning
- Purpose: To ensure that Transmission Operators and Balancing Authorities have plans for operating within specified limits.
- TOP-003-4: Operational Reliability Data
- Purpose: To ensure that the Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority have data needed to fulfill their operational and planning responsibilities.
- TOP-010-1(i): Real-time Reliability Monitoring and Analysis Capabilities
- Purpose: Establish requirements for Real-time monitoring and analysis capabilities to support reliable System operations.
Transmission Planning (TPL)
- TPL-001-4: Transmission System Planning Performance Requirements
- Purpose: Establish Transmission system planning performance requirements within the planning horizon to develop a Bulk Electric System (BES) that will operate reliably over a broad spectrum of System conditions and following a wide range of probable Contingencies.
- TPL-007-4: Transmission System Planned Performance for Geomagnetic Disturbance Events
- Purpose: Establish requirements for Transmission system planned performance during geomagnetic disturbance (GMD) events.
Voltage and Reactive (VAR)
- VAR-001-5: Voltage and Reactive Control
- Purpose: To ensure that voltage levels, reactive flows, and reactive resources are monitored, controlled, and maintained within limits in Real-time to protect equipment and the reliable operation of the Interconnection.
- VAR-002-4.1: Genorator Operation for Maintaining Network Voltage Schedules
- Purpose: To ensure generators provide reactive support and voltage control, within generating Facility capabilities, in order to protect equipment and maintain reliable operation of the Interconnection.
- VAR-501-WECC-3.1: Power Systems Stabilizer (PSS)
- Purpose: To ensure the Western Interconnection is operated in a coordinated manner under normal and abnormal conditions by establishing the performance criteria for WECC power system stabilizers.
Get Your NERC Compliance in Order Before you Face Audits
Certrec has helped over 120 generating facilities establish and maintain NERC Compliance Programs. We manage the entire NERC compliance program for 60+ registered sites in the US and Canada who trust us to decrease their regulatory and reputational risk. With Certrec as the regulatory compliance arm for your registered entity, you can focus on your core business while we monitor upcoming NERC standards, process paperwork, and ensure your entity remains NERC compliant.
Share
What are NERC Reliability Standards?
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s (NERC) Reliability Standards define the requirements for planning process and operations of the Bulk Electric System (BES). These standards are subject to enforcement within the United States and parts of Canada and Mexico. Reliability Standards establish threshold requirements for assuring the Bulk Electric System is planned, operated, and maintained to minimize risks of cascading failures, avoid damage to major equipment, or limit interruptions of the Bulk Power System (BPS).
The NERC standards consist of almost 100 standards across 14 different disciplines. NERC monitors and enforces compliance with these standards through six regional entities. These regional entities are:
- Midwest Reliability Organization (MRO)
- Northeast Power Coordinating Council (NPCC)
- Reliability First (RF)
- SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC)
- Texas Reliability Entity (Texas RE)
- Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC)
NERC Pillars for Success
The NERC reliability standards are built around four pillars for continued success. These pillars were developed in collaboration with the six regional entities. You can read more about NERC’s core values and strategies for success here. As defined by NERC, these pillars are:
- Reliability – to address events and identifiable risks, thereby ensuring the reliability of the BES
through proper mitigation and remediation. - Assurance – to provide assurance to the public, industry, and government for the reliable
performance of the BES. - Learning – to promote learning and continuous improvement of operations and adapt to lessons
learned for BES reliability. - Risk-Based Approach – to focus attention, resources, and actions on issues most important to BES
reliability.
Failure of NERC-registered entities to comply with these standards could result in grievous fines based on the severity and duration of the violation. When an organization is in violation of standards, the corresponding regional entities assess penalties and monitor approved mitigation plans for compliance. Listed below are the NERC Reliability Standards currently subject to enforcement and their purpose.
The NERC Reliability Standards:
Resource and Demand Balancing (BAL)
- BAL-001-2: Real Power Balancing Control Performance
- Purpose: To control Interconnection frequency within defined limits.
- BAL-001-TRE-1: Primary Frequency Response in the ERCOT Region
- Purpose: To maintain Interconnection steady-state frequency within defined limits
- BAL-001-TRE-2: Primary Frequency Response in the ERCOT Region
- Purpose: To maintain Interconnection steady-state frequency within defined limits.
- BAL-002-3: Disturbance Control Standard – Contingency Reserve for Recovery from a Balancing Contingency Event
- Purpose: To ensure the Balancing Authority or Reserve Sharing Group balances resources and demand and returns the Balancing Authority’s or Reserve Sharing Group’s Area Control Error to defined values (subject to applicable limits) following a Reportable Balancing Contingency Event.
- BAL-002-WECC-2a: Contingency Reserve
- Purpose: To specify the quantity and types of Contingency Reserve required to ensure reliability under normal and abnormal conditions.
- BAL-002-WECC-3: Contingency Reserve
- Purpose: To specify the quantity and types of Contingency Reserve required to ensure reliability under normal and abnormal conditions.
- BAL-003-2: Frequency Response and Frequency Bias Setting
- Purpose: To require sufficient Frequency Response from the Balancing Authority (BA) to maintain Interconnection Frequency within predefined bounds by arresting frequency deviations and supporting frequency until the frequency is restored to its scheduled value. To provide consistent methods for measuring Frequency Response and determining the Frequency Bias Setting.
- BAL-0040-WECC-3: Automatic Time Error Correction
- Purpose: To maintain Interconnection frequency and to ensure that Time Error Corrections and Primary Inadvertent Interchange (PII) payback are effectively conducted in a manner that does not adversely affect the reliability of the Interconnection.
- BAL-005-1: Balancing Authority Control
- Purpose: This standard establishes requirements for acquiring data necessary to calculate Reporting Area Control Error (Reporting ACE). The standard also specifies a minimum periodicity, accuracy, and availability requirement for acquisition of the data and for providing the information to the System Operator.
- BAL-502-RF-03: Planning Resource Adequacy Analysis, Assessment and Documentation
- Purpose: To establish common criteria, based on “one day in ten year” loss of Load expectation principles, for the analysis, assessment and documentation of Resource Adequacy for Load in the ReliabilityFirst Corporation (RF) region
Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP)
- CIP-002-5.1a: Cyber Security – BES Cyber System Categorization
- Purpose: To identify and categorize BES Cyber Systems and their associated BES Cyber Assets for the application of cyber security requirements commensurate with the adverse impact that loss, compromise, or misuse of those BES Cyber Systems could have on the reliable operation of the BES. Identification and categorization of BES Cyber Systems support appropriate protection against compromises that could lead to misoperation or instability in the BES.
- CIP-003-8: Cyber Security – Security Management Controls
- Purpose: To specify consistent and sustainable security management controls that establish responsibility and accountability to protect BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-004-6: Cyber Security – Personnel & Training
- Purpose: To minimize the risk against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES) from individuals accessing BES Cyber Systems by requiring an appropriate level of personnel risk assessment, training, and security awareness in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems.
- CIP-005-7: Cyber Security – Electronic Security Perimeter(s)
- Purpose: To manage electronic access to BES Cyber Systems by specifying a controlled Electronic Security Perimeter in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the BES.
- CIP-006-6: Cyber Security – Physical Security of BES Cyber Systems
- Purpose: To manage physical access to Bulk Electric System (BES) Cyber Systems by specifying a physical security plan in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the BES.
- CIP-007-6: Cyber Security – System Security Management
- Purpose: To manage system security by specifying select technical, operational, and procedural requirements in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-008-6: Cyber Security – Incident Reporting and Response Planning
- Purpose: To mitigate the risk to the reliable operation of the BES as the result of a Cyber Security Incident by specifying incident response requirements.
- CIP-009-6: Cyber Security – Recovery Plans for BES Cyber Systems
- Purpose: To recover reliability functions performed by BES Cyber Systems by specifying recovery plan requirements in support of the continued stability, operability, and reliability of the BES.
- CIP-10-4: Cyber Security – Configuration Change Management and Vulnerability Assessments
- Purpose: To prevent and detect unauthorized changes to BES Cyber Systems by specifying configuration change management and vulnerability assessment requirements in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems from compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-011-2: Cyber Security – Information Protection
- Purpose: To prevent unauthorized access to BES Cyber System Information by specifying information protection requirements in support of protecting BES Cyber Systems against compromise that could lead to misoperation or instability in the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- CIP-012-1: Cyber Security – Communications between Control Centers
- Purpose: To protect the confidentiality and integrity of Real-time Assessment and Real-time monitoring data transmitted between Control Centers.
- CIP-013-2: Cyber Security – Supply Chain Risk Management
- Purpose: To mitigate cyber security risks to the reliable operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) by implementing security controls for supply chain risk management of BES Cyber Systems.
- CIP-014-3: Physical Security
- Purpose: To identify and protect Transmission stations and Transmission substations, and their associated primary control centers, that if rendered inoperable or damaged as a result of a physical attack could result in instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading within an
Interconnection
- Purpose: To identify and protect Transmission stations and Transmission substations, and their associated primary control centers, that if rendered inoperable or damaged as a result of a physical attack could result in instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading within an
Communications (COM)
- COM-001-3: Communications
- Purpose: To establish Interpersonal Communication capabilities necessary to maintain reliability.
- COM-002-4: Operating Personnel Communications Protocols
- Purpose: To improve communications for the issuance of Operating Instructions with predefined communications protocols to reduce the possibility of miscommunication that could lead to action or inaction harmful to the reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES)
Emergency Preparedness and Operations (EOP)
- EOP-004-4: Event Reporting
- Purpose: To improve the reliability of the Bulk Electric System by requiring the reporting of events by Responsible Entities.
- EOP-005-3: System Restoration from Blackstart Resources
- Purpose: Ensure plans, Facilities, and personnel are prepared to enable System restoration from Blackstart Resources to ensure reliability is maintained during restoration and priority is placed on restoring the Interconnection.
- EOP-006-3: System Restoration Coordination
- Purpose: Ensure plans are established and personnel are prepared to enable effective coordination of the System restoration process to ensure reliability is maintained during restoration and priority is placed on restoring the Interconnection.
- EOP-008-2: Loss of Control Center Functionality
- Purpose: Ensure continued reliable operations of the Bulk Electric System (BES) in the event that a control center becomes inoperable.
- EOP-10-1: Geomagnetic Disturbance Operations
- Purpose: To mitigate the effects of geomagnetic disturbance (GMD) events by implementing Operating Plans, Processes, and Procedures.
- EOP-011-1: Emergency Operations
- Purpose: To address the effects of operating Emergencies by ensuring each Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority has developed Operating Plan(s) to mitigate operating Emergencies, and that those plans are coordinated within a Reliability Coordinator Area.
- EOP-011-2: Emergency Preparedness and Operations
- Purpose: To ensure each Transmission Operator, Balancing Authority, and Generator Owner has developed plan(s) to mitigate and prepare for operating Emergencies; and that Operating Plans are coordinated within a Reliability Coordinator Area.
Facilities Design, Connections, and Maintenance (FAC)
- FAC-001-3: Facility Interconnection Requirements
- Purpose: To avoid adverse impacts on the reliability of the Bulk Electric System, Transmission Owners and applicable Generator Owners must document and make Facility interconnection requirements available so that entities seeking to interconnect will have the necessary information.
- FAC-002-3: Facility Interconnection Studies
- Purpose: To study the impact of interconnecting new or materially modified Facilities on the Bulk Electric System.
- FAC-003-4: Transmission Vegetation Management
- Purpose: To maintain a reliable electric transmission system by using a defense-in-depth strategy to manage vegetation located on transmission rights of way (ROW) and minimize encroachments from vegetation located adjacent to the ROW, thus preventing the risk of those vegetation- related outages that could lead to Cascading.
- FAC-008-5: Facility Ratings
- Purpose: To ensure that Facility Ratings used in the reliable planning and operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on technically sound principles. A Facility Rating is essential for the determination of System Operating Limits.
- FAC-010-3: System Operating Limits Methodology for the Planning Horizon
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operating Limits (SOLs) used in the reliable planning of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on an established methodology or methodologies.
- FAC-011-3: System Operating Limits Methodology got the Operation Horizon
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operating Limits (SOLs) used in the reliable operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on an established methodology or methodologies.
- FAC-014-2: Establish and Communicate System Operating Limits
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operating Limits (SOLs) used in the reliable planning and operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are determined based on an established methodology or methodologies.
- FAC-501-WECC-2: Transmission Maintenance
- Purpose: To ensure the Transmission Owner of a transmission path identified in Attachment B, Major WECC Transfer Paths in the Bulk Electric System, including associated facilities has a Transmission Maintenance and Inspection Plan (TMIP); and performs and documents maintenance and inspection activities in accordance with the TMIP.
Interchange Scheduling and Coordination (INT)
- INT-006-5: Evaluation of Interchange Transactions
- Purpose: To ensure that responsible entities conduct a reliability assessment of each Arranged Interchange before it is implemented.
- INT-009-3: Implementation of Interchange
- Purpose: To ensure that Balancing Authorities implement the Interchange as agreed upon in the Interchange confirmation process.
Interconnection Reliability Operations and Coordination (IRO)
- IRO-001-4: Reliability Coordination – Responsibilities and Authorities
- Purpose: To establish the responsibility of Reliability Coordinators to act or direct other entities to act.
- IRO-002-4: Reliability Coordination – Monitoring and Analysis
- Purpose: Provide System Operators with the capabilities necessary to monitor and analyze data needed to perform their reliability functions.
- IRO-002-7: Reliability Coordination – Monitoring and Analysis
- Purpose: To provide System Operators with the capabilities necessary to monitor and analyze data needed to perform their reliability functions.
- IRO-006-5: Reliability Coordination – Transmission Loading Relief (TLR)
- Purpose: To ensure coordinated action between Interconnections when implementing Interconnection-wide transmission loading relief procedures to prevent or manage potential or actual SOL and IROL exceedances to maintain reliability of the bulk electric system.
- IRO-006-EAST-2: Transmission Loading Relief Procedure for the Eastern Connection
- Purpose: To coordinate action between Reliability Coordinators within the Eastern
Interconnection when implementing transmission loading relief procedures (TLR) for the Eastern Interconnection to prevent or manage potential or actual System Operating Limit (SOL) and Interconnection Reliability Operating Limit (IROL) exceedances to maintain reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- Purpose: To coordinate action between Reliability Coordinators within the Eastern
- IRO-006-WECC-3: Qualified Path Unscheduled Flow (USF) Relief
- Purpose: To mitigate flows on Qualified Paths to reliable levels during Real-time operations.
- IRO-008-2: Reliability Coordinator Operational Analyses and Real-time Assessments
- Purpose: Perform analyses and assessments to prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading.
- IRO-009-2 Reliability Coordinator Actions to Operate Within IROLs
- Purpose: To prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or cascading outages that adversely impact the reliability of the interconnection by ensuring prompt action to prevent or mitigate instances of exceeding Interconnection Reliability Operating Limits (IROLs).
- IRO-010-3: Reliability Coordinator Data Specification and Collection
- Purpose: To prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading outages that adversely impact reliability, by ensuring the Reliability Coordinator has the data it needs to monitor and assess the operation of its Reliability Coordinator Area.
- IRO-014-3: Coordination Among reliability Coordinators
- Purpose: To ensure that each Reliability Coordinator’s operations are coordinated such that they will not adversely impact other Reliability Coordinator Areas and to preserve the reliability benefits of interconnected operations.
- IRO-017-1: Outage Coordination
- Purpose: To ensure that outages are properly coordinated in the Operations Planning time horizon and Near-Term Transmission Planning Horizon.
- IRO-018-1(i): Reliability Coordinator Real-time Reliability Monitoring and Analysis
- Purpose: Establish requirements for Real-time monitoring and analysis capabilities to support reliable System operations.
Modeling, Data, and Analysis (MOD)
- MOD-001-1a: Available Transmission System Capability
- Purpose: To ensure that calculations are performed by Transmission Service Providers to maintain awareness of available transmission system capability and future flows on their own systems as well as those of their neighbors
- MOD-004-1: Capacity Benefit Margin
- Purpose: To promote the consistent and reliable calculation, verification, preservation, and use of Capacity Benefit Margin (CBM) to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-008-1: Transmission Reliability Margin Calculation Methodology
- Purpose: To promote the consistent and reliable calculations, verification, preservation, and use of Transmission Reliability Margin (TRM) to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-025-2: Verification and Data Reporting of Generator Real and Reactive Power Capability and Synchronous Condenser Reactive Power Capability
- Purpose: To ensure that accurate information on generator gross and net Real and Reactive Power capability and synchronous condenser Reactive Power capability is available for planning models used to assess Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability.
- MOD-026-1: Verification of Models and Data for Generator Excitation Control System or Plant Volt/Var Control Functions
- Purpose: To verify that the generator excitation control system or plant volt/var control function model (including the power system stabilizer model and the impedance compensator model) and the model parameters used in dynamic simulations accurately represent the generator excitation control system or plant volt/var control function behavior when assessing Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability.
- MOD-027-1: Verification of Models and Data for Turbine/Governor and Load Control or Active Power/Frequency Control Functions
- Purpose: To verify that the turbine/governor and load control or active power/frequency control model and the model parameters, used in dynamic simulations that assess Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability, accurately represent generator unit real power response to system frequency variations.
- MOD-028-2: Area Interchange Methodology
- Purpose: To increase consistency and reliability in the development and documentation of Transfer Capability calculations for short-term use performed by entities using the Area Interchange Methodology to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-029-2a: Rated System Path Methodology
- Purpose: To increase consistency and reliability in the development and documentation of transfer capability calculations for short-term use performed by entities using the Rated System Path Methodology to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-30-3: Flowgate Methodology
- Purpose: To increase consistency and reliability in the development and documentation of transfer capability calculations for short-term use performed by entities using the Flowgate Methodology to support analysis and system operations.
- MOD-31-3: Demand and Energy Data
- Purpose: To provide authority for applicable entities to collect Demand, energy and related data to support reliability studies and assessments and to enumerate the responsibilities and obligations of requestors and respondents of that data.
- MOD-032-1: Data for Power System, Modeling and Analysis
- Purpose: To establish consistent modeling data requirements and reporting procedures for development of planning horizon cases necessary to support analysis of the reliability of the interconnected transmission system.
- MOD-033-2: Steady-State and Dynamic System Model Validation
- Purpose: To establish consistent validation requirements to facilitate the collection of accurate data and building of planning models to analyze the reliability of the interconnected transmission system.
Nuclear (NUC)
- NUC-001-4: Nuclear Plant Interface Coordination
- Purpose: This standard requires coordination between Nuclear Plant Generator Operators and Transmission Entities for the purpose of ensuring nuclear plant safe operation and shutdown.
Personnel Performance, Training, and Qualifications (PER)
- PER-003-2: Operating Personnel Credentials
- Purpose: To ensure that System Operators performing the reliability-related tasks of the Reliability Coordinator, Balancing Authority and Transmission Operator are certified through the NERC System Operator Certification Program when filling a Real- time operating position responsible for control of the Bulk Electric System.
- PER-005-2: Operations Personnel Training
- Purpose: To ensure that personnel performing or supporting Real-time operations on the Bulk Electric System are trained using a systematic approach.
- PER-006-1: Specific Training for Personnel
- Purpose: To ensure that personnel are trained on specific topics essential to reliability to perform or support Real-time operations of the Bulk Electric System.
Protection and Control (PRC)
- PRC-002-2: Disturbance Monitoring and Reporting Requirements
- Purpose: To have adequate data available to facilitate analysis of Bulk Electric System (BES) Disturbances.
- PRC-004-6: Protection System Misoperation Identification and Correction
- Purpose: Identify and correct the causes of Misoperations of Protection Systems for Bulk Electric System (BES) Elements.
- PRC-005-1.1b: Transmission and Generation Protection System Maintenance and Testing
- Purpose: To ensure all transmission and generation Protection Systems affecting the reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES) are maintained and tested.
- PRC-005-6: Protection System, Automatic Reclosing, and Sudden Pressure Relaying Maintenance
- Purpose: To document and implement programs for the maintenance of all Protection Systems, Automatic Reclosing, and Sudden Pressure Relaying affecting the reliability of the Bulk Electric System (BES) so that they are kept in working order.
- PRC-006-5: Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding
- Purpose: To establish design and documentation requirements for automatic underfrequency load shedding (UFLS) programs to arrest declining frequency, assist recovery of frequency following underfrequency events and provide last resort system preservation measures.
- PRC-006-NPCC-2: Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding
- Purpose: The NPCC Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding (UFLS) regional Reliability Standard establishes more stringent and specific NPCC UFLS program requirements than the NERC continent–wide PRC–006 standard. The program is designed such that declining frequency is arrested and recovered in accordance with established NPCC performance requirements stipulated in this document.
- PRC-006-SERC-02: Automatic Underfrequency Load Shedding Requirements
- Purpose: To establish consistent and coordinated requirements for the design, implementation, and analysis of automatic underfrequency load shedding (UFLS) programs among all SERC applicable entities.
- PRC-008-0: Implementation and Documentation of Underfrequency Load Shedding Equipment Maintenance Program
- Purpose: Provide last resort system preservation measures by implementing an Under Frequency Load Shedding (UFLS) program.
- PRC-010-2: Undervoltage Load Shedding
- Purpose: To establish an integrated and coordinated approach to the design, evaluation, and reliable operation of Undervoltage Load Shedding Programs (UVLS Programs).
- PRC-011-0: Undervoltage Load Shedding System Maintenance and Testing
- Purpose: Provide system preservation measures in an attempt to prevent system voltage collapse or voltage instability by implementing an Undervoltage Load Shedding (UVLS) program.
- PRC-012-2: Remedial Action Schemes
- Purpose: To ensure that Remedial Action Schemes (RAS) do not introduce unintentional or unacceptable reliability risks to the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- PRC-017-1: Remedial Action Scheme Maintenance and Testing
- Purpose: To ensure that all Remedial Action Schemes (RAS) are properly designed, meet performance requirements, and are coordinated with other protection systems. To ensure that
maintenance and testing programs are developed and misoperations are analyzed and corrected.
- Purpose: To ensure that all Remedial Action Schemes (RAS) are properly designed, meet performance requirements, and are coordinated with other protection systems. To ensure that
- PRC-018-1: Disturbance Monitoring Equipment Installation and Data Reporting
- Purpose: Ensure that Disturbance Monitoring Equipment (DME) is installed and that Disturbance data is reported in accordance with regional requirements to facilitate analyses of events.
- PRC-019-2: Coordination of Generating Unit or Plant Capabilities, Voltage Regulating Controls, and Protection
- Purpose: To verify coordination of generating unit Facility or synchronous condenser voltage regulating controls, limit functions, equipment capabilities and Protection System settings.
- PRC-023-4: Transmission Relay Loadability
- Purpose: Protective relay settings shall not limit transmission loadability; not interfere with system operators’ ability to take remedial action to protect system reliability and; be set to reliably detect all fault conditions and protect the electrical network from these faults.
- PRC-024-3: Frequency and Voltage Protection Settings for Generating Resources
- Purpose: To set protection such that generating resource(s) remain connected during defined frequency and voltage excursions in support of the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- PRC-025-2: Generator Relay Loadability
- Purpose: To set load-responsive protective relays associated with generation Facilities at a level to prevent unnecessary tripping of generators during a system disturbance for conditions that do not pose a risk of damage to the associated equipment.
- PRC-026-1: Relay Performance During Stable Power Swings
- Purpose: To ensure that load-responsive protective relays are expected to not trip in response to stable power swings during non-Fault conditions.
- PRC-027-1: Coordination of Protection Systems for Performance During Faults
- Purpose: To maintain the coordination of Protection Systems installed to detect and isolate Faults on Bulk Electric System (BES) Elements, such that those Protection Systems operate in the intended sequence during Faults.
Transmission Operations (TOP)
- TOP-001-5: Transmission Operations
- Purpose: To prevent instability, uncontrolled separation, or Cascading outages that adversely impact the reliability of the Interconnection by ensuring prompt action to prevent or mitigate such occurrences.
- TOP-002-4: Operations Planning
- Purpose: To ensure that Transmission Operators and Balancing Authorities have plans for operating within specified limits.
- TOP-003-4: Operational Reliability Data
- Purpose: To ensure that the Transmission Operator and Balancing Authority have data needed to fulfill their operational and planning responsibilities.
- TOP-010-1(i): Real-time Reliability Monitoring and Analysis Capabilities
- Purpose: Establish requirements for Real-time monitoring and analysis capabilities to support reliable System operations.
Transmission Planning (TPL)
- TPL-001-4: Transmission System Planning Performance Requirements
- Purpose: Establish Transmission system planning performance requirements within the planning horizon to develop a Bulk Electric System (BES) that will operate reliably over a broad spectrum of System conditions and following a wide range of probable Contingencies.
- TPL-007-4: Transmission System Planned Performance for Geomagnetic Disturbance Events
- Purpose: Establish requirements for Transmission system planned performance during geomagnetic disturbance (GMD) events.
Voltage and Reactive (VAR)
- VAR-001-5: Voltage and Reactive Control
- Purpose: To ensure that voltage levels, reactive flows, and reactive resources are monitored, controlled, and maintained within limits in Real-time to protect equipment and the reliable operation of the Interconnection.
- VAR-002-4.1: Genorator Operation for Maintaining Network Voltage Schedules
- Purpose: To ensure generators provide reactive support and voltage control, within generating Facility capabilities, in order to protect equipment and maintain reliable operation of the Interconnection.
- VAR-501-WECC-3.1: Power Systems Stabilizer (PSS)
- Purpose: To ensure the Western Interconnection is operated in a coordinated manner under normal and abnormal conditions by establishing the performance criteria for WECC power system stabilizers.
Get Your NERC Compliance in Order Before you Face Audits
Certrec has helped over 120 generating facilities establish and maintain NERC Compliance Programs. We manage the entire NERC compliance program for 60+ registered sites in the US and Canada who trust us to decrease their regulatory and reputational risk. With Certrec as the regulatory compliance arm for your registered entity, you can focus on your core business while we monitor upcoming NERC standards, process paperwork, and ensure your entity remains NERC compliant.
Just Getting Started with Nerc? Check Out Some of Our Resources
NERC Common Questions and Answers
What is the difference between FERC and NERC? The Federal...
Read MoreNERC Standards: NERC CIP Explained for the Energy Sector
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) mandate encompasses technical...
Read More